Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Trigonometry - non-right angled triangles.
The Sine Rule and the Cosine Rule.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
This page introduces the information and explanations in the pages and the videos on the Sine Rule and the Cosine Rule.
Comparison between the two rules.
In triangles without a right angle - certainly the most common shape for a triangle - we cannot use the usual basic ratios we have defined to far. For example, there can be no hypotenuse in these triangles.
Therefore we need to develop strategies to enable the calculation of the sizes of sides and angles.
The two rules referred to as the Sine Rule and the Cosine Rule are the common strategies. They are applied depending what information we have about a triangle:
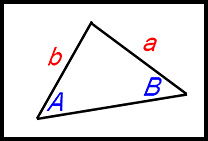
| Sine Rule | Used when we have a triangle with:
and we have to find the size of one of these. |
 |
| Cosine Rule | Used when we have a triangle with;
and we have to find the size of one of these. |
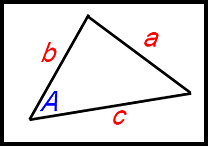 |
So to select the appropriate Rule becomes essentially the simple task of counting how many angles are indicated in the diagram or in the problem.
Proofs of each rule are provided separately for the Sine Rule and for the Cosine Rule.